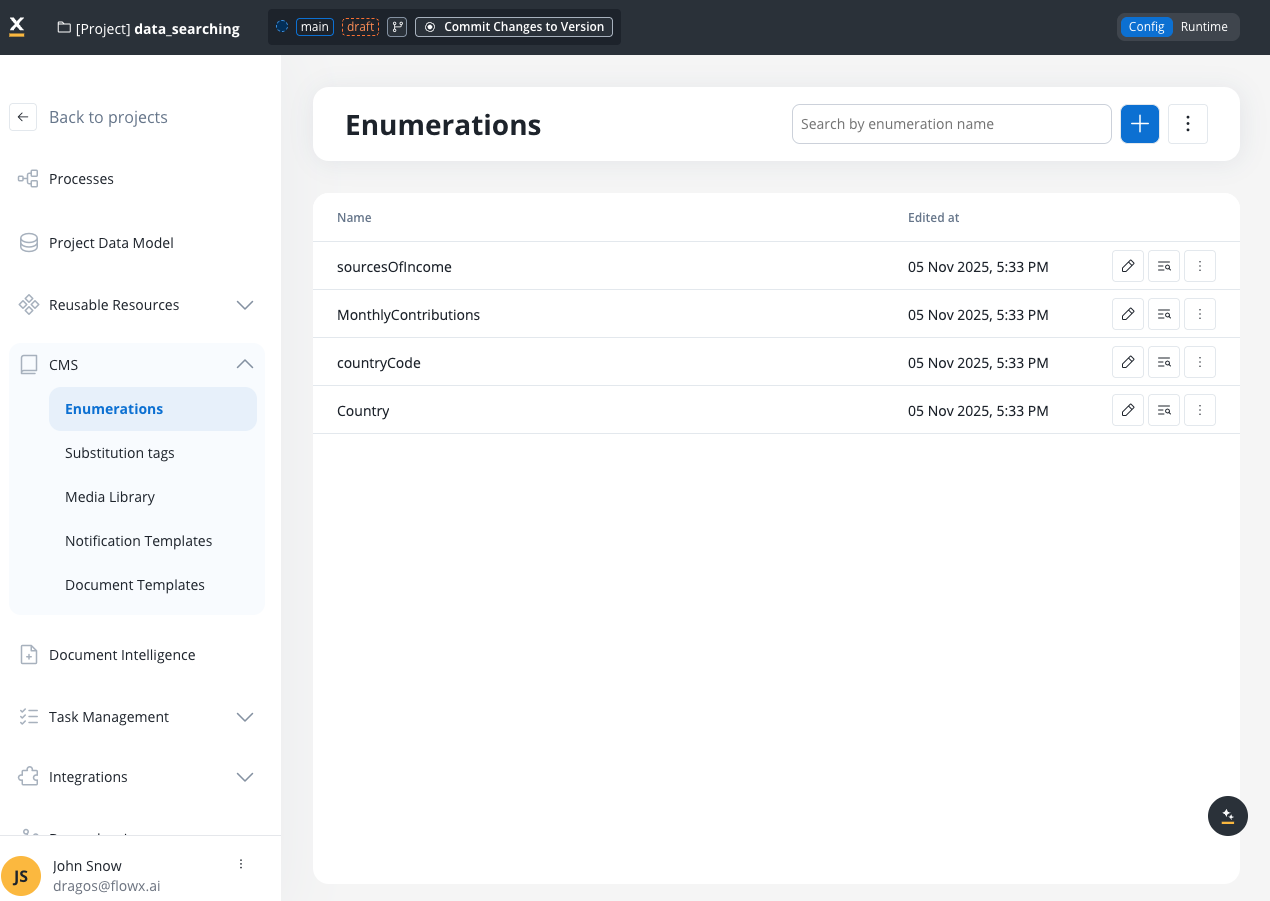
Key features
The FlowX.AI CMS offers the following features:Enumerations
Manage and configure enumerations for various content types
Substitution tags
Utilize tags to dynamically insert content values. Essential for Task Management localization with 51 system tags
Media library
Organize and manage media assets
Notification templates
Manage notification templates
Document templates
Manage document templates
Enumeration sources
The FlowX.AI platform supports three types of enumeration sources:- Project-level enumerations: Enumerations defined directly at the project level within the FlowX.AI Designer
- Library enumerations: Enumerations defined in a shared library that must be set as a dependency for the project
- Data source enumerations: Enumerations that come from external data sources when using the Enumeration Mapper feature
Deployment and integration
The CMS can be rapidly deployed on your chosen infrastructure, preloaded with necessary taxonomies or content via a REST interface, and integrated with the FlowX Engine using Kafka events. For deployment and configuration, refer to the:CMS setup guide
Using the CMS service
Once the CMS is deployed in your infrastructure, you can define and manage custom content types, such as lists with different values based on external systems, blog posts, and more.Kafka integration
You can use Kafka to translate and extract content values based on your defined languages and source systems. This is useful for:- Extracting values from specific enumerations for UI components
- Sending data to other integrations that require different label formats
- Generating documents with localized content
- Handling different label conventions from various external systems
Various external systems and integrations might use different labels for the same information. In processes, it is easier to use the corresponding code and translate this into the needed label when necessary: for example when sending data to other integrations, when generating documents, etc.
Kafka topics configuration
Manage content retrieval messages between the CMS and the FlowX Engine using the following Kafka topics:| Environment Variable | Default FlowX.AI value (customizable) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| KAFKA_TOPIC_REQUEST_CONTENT_IN | ai.flowx.dev.plugin.cms.trigger.retrieve.content.v1 | Topic where CMS listens for incoming content retrieval requests |
| KAFKA_TOPIC_REQUEST_CONTENT_OUT | ai.flowx.dev.engine.receive.plugin.cms.retrieve.content.results.v1 | Topic where CMS sends content retrieval results back to FlowX Engine |
Required Kafka headers
The following headers must be included in translation requests:| Header | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
BUILD_APP_VERSION_ID | Yes* | Application version build ID |
BUILD_ID | Yes* | Alternative to BUILD_APP_VERSION_ID |
WORKSPACE_ID | No | Workspace identifier for multi-tenant environments |
Translation request structure
Add a Send Message Task (kafka send event) and configure it to send content requests to the FlowX.AI Engine.Request parameters
| Parameter | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
sourceSystem | String | No* | Target source system for code translation |
fromSourceSystem | String | No* | Source system to translate codes from (cannot be used with sourceSystem) |
language | String | No* | Language code for label translation (e.g., “en”, “fr”, “ro”) |
replyTopic | String | No | Custom Kafka topic for response (overrides default) |
entries | Array | Yes | List of content entries to translate |
Entry structure
Each entry in theentries array contains:
| Parameter | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
codes | Array | Yes | Array of codes to translate |
contentDescription | Object | Yes | Content metadata for lookup |
contentDescription.name | String | Yes | Enumeration/content name |
contentDescription.application | String | No | Application name (defaults to defaultApplication) |
children | Object | No | Nested child content translations (hierarchical) |
Example: Basic translation request
Request Body: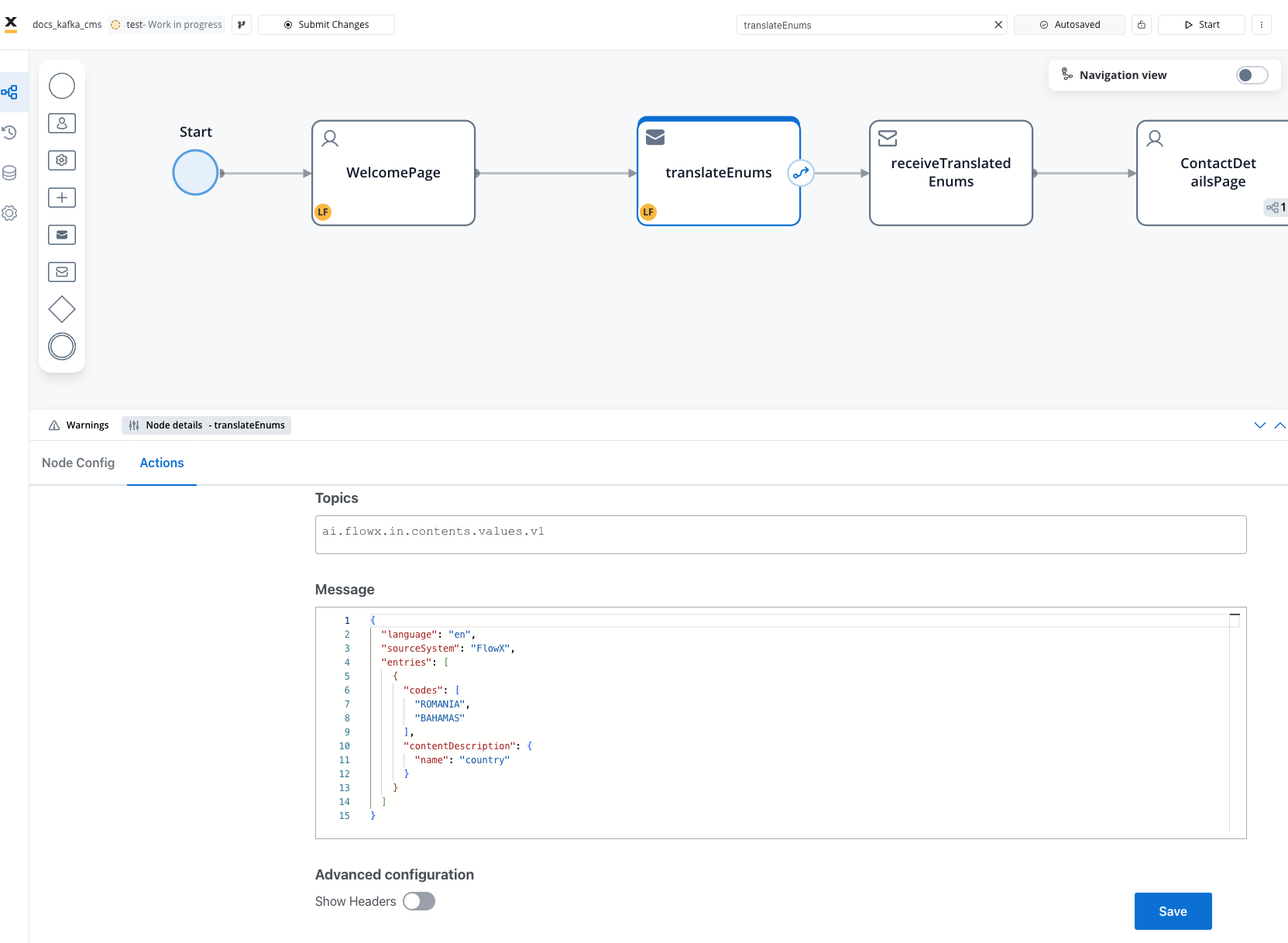
Example: Hierarchical content request
For enumerations with nested/hierarchical structures (parent-child relationships), you can request content at multiple levels by specifying thechildren property. This is useful when you need to retrieve values from dependent dropdowns or cascading selections.
Use cases:
- Country → County → City selections
- Product Category → Subcategory → Product
- Department → Team → Employee
- Any cascading dropdown scenario
- The
childrenproperty is an object where keys represent parent codes and values are arrays of child items - Each child item must have a
codeproperty and can optionally have a nestedchildrenarray for deeper hierarchies - This allows you to request specific branches of hierarchical data rather than entire enumerations
- Content metadata (name, application) is inferred from parent-child relationships configured in CMS
- Unlimited nesting depth is supported for complex hierarchical structures
Translation types
The CMS translation service supports multiple types of translations:- Language Translation
- Source System Translation
- Combined Translation
- Reverse Translation
Purpose: Translate codes to human-readable labels in specific languagesRequest:Response:
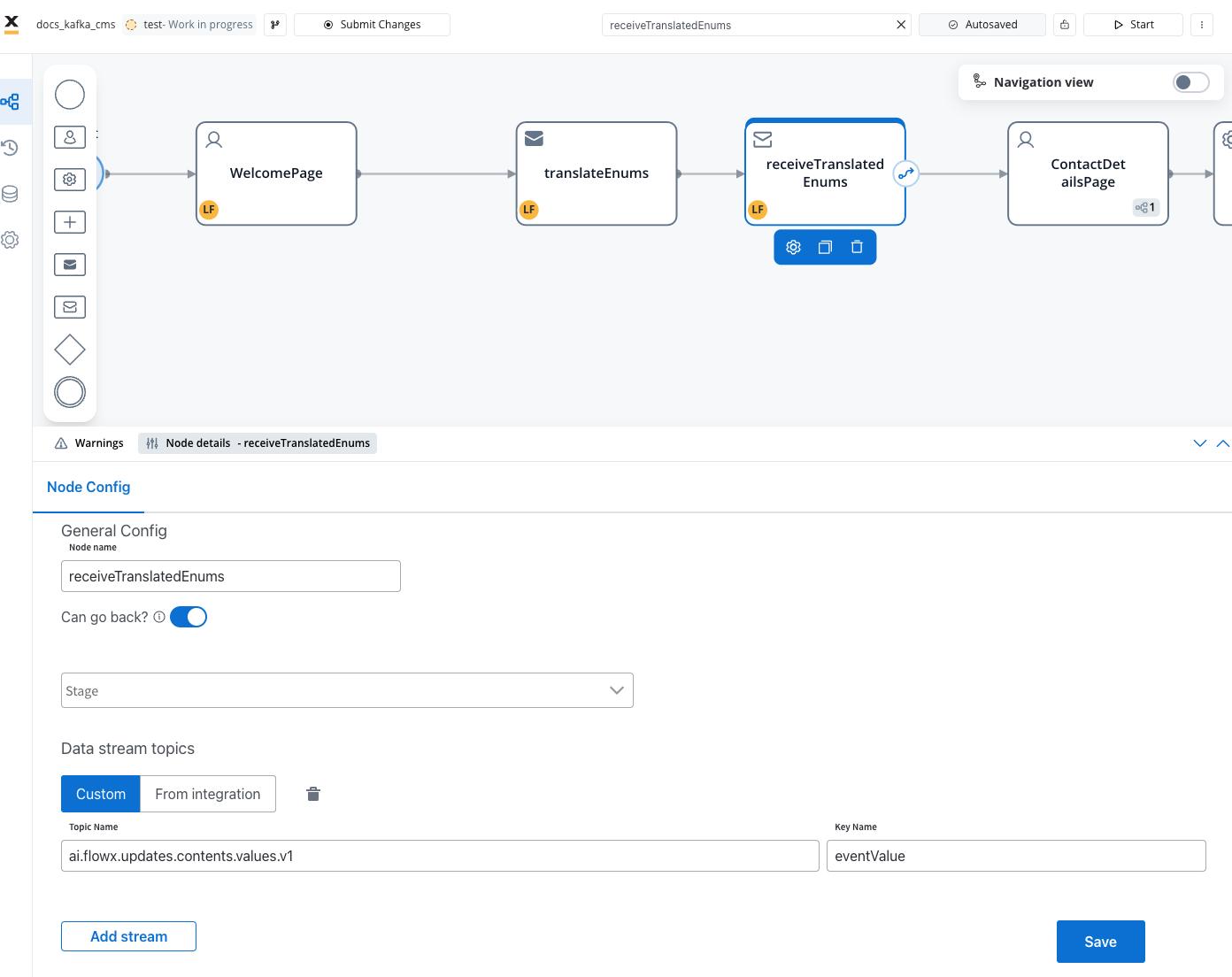
Translation response structure
Add a Receive Message Task to handle the response from the CMS service. Configure it to listen to the topic where the Engine sends the response (e.g.,ai.flowx.updates.contents.values.v1).
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
entries | Array | List of translated content entries |
entries[].contentName | String | Name of the content/enumeration |
entries[].code | String | Original code value |
entries[].label | String | Translated label based on language parameter |
entries[].translatedCode | String | Code translated for source system (format: {code}-{sourceSystem}) |
entries[].children | Object | Nested translated child content (for hierarchical requests) |
error | String | Error message (null if successful) |
Dynamic language switching example
Advanced features
Custom reply topics
You can override the default response topic by specifying areplyTopic parameter in your request:
- Process-specific handling
- Asynchronous workflows
- Custom routing logic
Build context and versioning
The CMS translation service uses build context headers to ensure correct content version resolution:BUILD_APP_VERSION_IDorBUILD_IDensures translation uses the correct content version- Critical for environments with multiple application versions running simultaneously
- Resolves content from build manifest resource overrides
- Ensures consistent translations across deployments
Resource overrides
The translation service supports content overrides via build manifest, enabling:- Version-specific translations
- Multi-tenant workspace configurations
- Environment-specific content variations
- A/B testing with different content versions
Performance considerations
Batch Multiple Codes
Batch Multiple Codes
Request multiple codes in a single Kafka message to reduce overhead:
Use Hierarchical Children
Use Hierarchical Children
Request parent and child content together to minimize round trips:
Cache Translated Values
Cache Translated Values
Store translated values in process data when they will be reused multiple times within the same process instance.
Progressive Loading
Progressive Loading
For deep hierarchies, load levels progressively based on user selections rather than requesting entire hierarchies upfront.
Error handling
Common translation errors:| Error | Description | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| Content not found | The specified content/enumeration does not exist | Verify content name and ensure it’s published in CMS |
| Invalid source system | The source system is not configured | Check source system configuration in CMS |
| Missing required fields | Required parameters are missing from request | Ensure codes and contentDescription.name are provided |
| Build context missing | Required headers not present | Include BUILD_APP_VERSION_ID or BUILD_ID in headers |
| Validation conflict | Both sourceSystem and fromSourceSystem provided | Use only one direction of translation per request |
When translation fails, the
error field contains a descriptive message and the entries array may be empty or contain partial results.

