Overview
Permission-based expressions enable you to:- Customize UI per role: Different roles see different UI elements within the same process
- Enable read-only access: Users view and navigate process instances without making changes
- Support concurrent work: Multiple users with different permissions work on the same instance
- Adapt dynamically: UI changes in real-time based on user permissions and process data
Use case examples: A loan application where applicants see only input fields, reviewers see approval buttons, and managers see all data but in read-only mode. One process definition serves all roles.
Prerequisites
Before configuring permission-based expressions:- Process definition created with swimlanes configured
- User roles defined in the platform
- Allow multiple executors enabled at the swimlane level (in process Settings → Permissions tab)
- Understanding of your access control requirements
Permission capabilities
Partial editing
Tailor UI element access for specific users, roles, or usernames within the same swimlane:- Role-based control: Different roles see different UI elements
- Username-specific access: Individual users get customized interfaces
- Data-driven permissions: Process data determines what users can access
Read-only access
Enable users to view and navigate process instances without modification:- Users can navigate through user tasks and view data
- All input fields and buttons are non-interactive
- Hide and disable conditions continue to apply
- Navigation between tasks remains available
Multiple executors
Multiple users with different roles work concurrently on the same process instance within a swimlane:- Different permission levels (Execute, Self-assign, View) assigned to different roles
- Each user sees their role-specific interface
- Changes are synchronized across all active users
- Essential for collaborative workflows with varied responsibilities
How permissions work
Permission-based expressions combine three key elements to control UI behavior:1. Swimlane role configuration
Configure base permissions at the swimlane level:- Assign roles (Execute, Self-assign, View) to user groups
- Enable Allow multiple executors to activate permission-based expressions
- Set minimum access level for each role
2. UI element conditions
Apply conditions to individual UI components to control visibility and interaction: Hide condition- Completely removes the UI element from the interface
- Available for all component types
- Element doesn’t occupy any space in the layout
- Shows the element but prevents user interaction
- Available for forms, form elements, and buttons
- Element appears grayed out or visually disabled
3. Condition precedence
When both hide and disable conditions exist on the same element, disable takes precedence. The element will be shown in a disabled state rather than hidden.
Configuring permission-based expressions
Follow these steps to set up permission-based UI control for your process:1
Enable multiple executors
Navigate to Process Settings → Permissions tab and enable Allow multiple executors for your swimlane.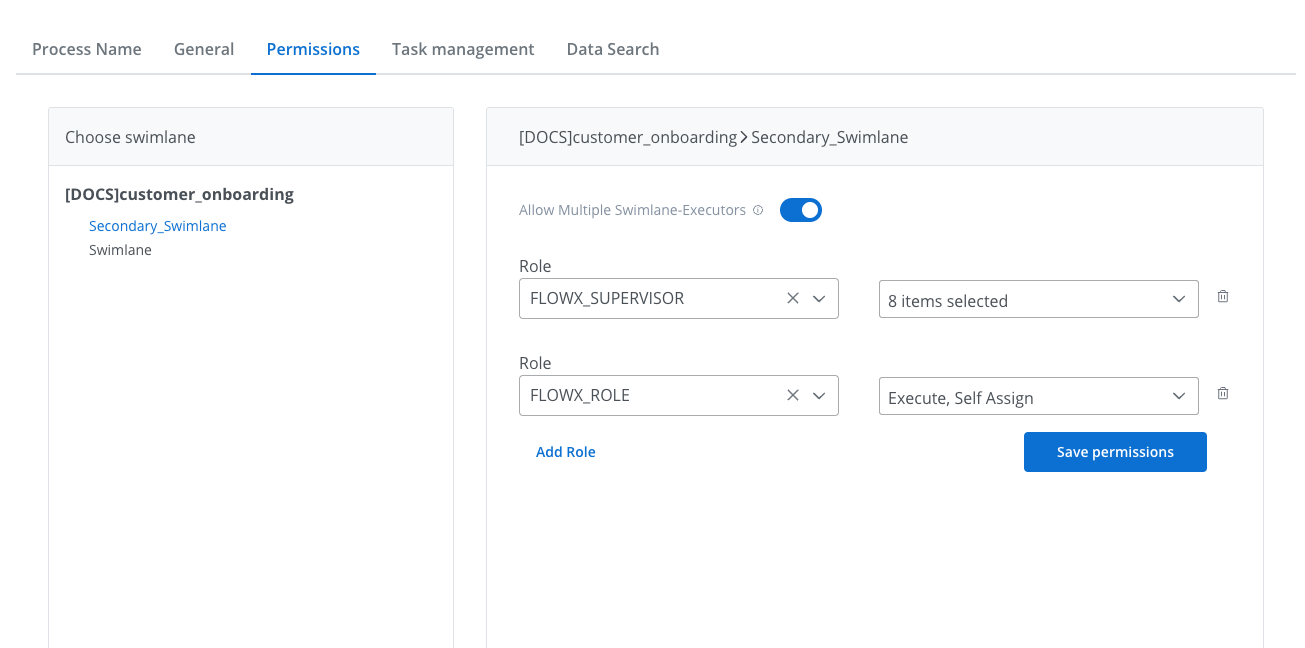

Enable multiple executors at the swimlane level
Configure role permissions (Execute, Self-assign, View) for each role that will access this swimlane.
2
Open UI Designer
Navigate to the UI Designer tab and select the component you want to configure with permission-based visibility or interaction controls.
3
Access permissions configuration
In the component properties panel, expand the Permissions section.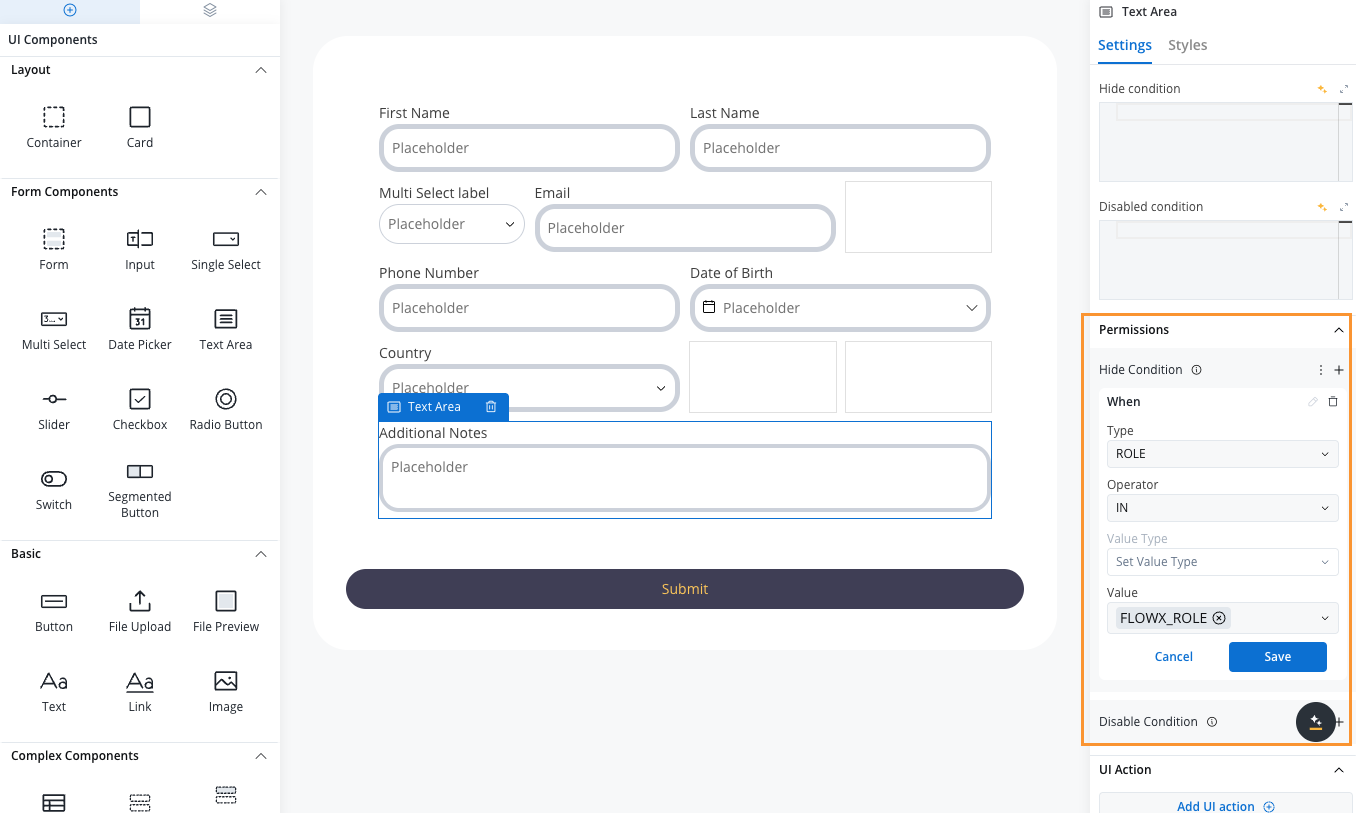

Permission configuration interface
4
Add condition
Click the + button next to your desired condition type:
- Hide Condition: Available for all component types
- Disable Condition: Available for forms, form elements, and buttons
5
Configure condition parameters
Define the permission logic using these parameters:Type: Who the condition applies to
- USERNAME: Target specific usernames
- ROLE: Target users with specific roles
- IN: Condition applies when user matches the value
- NOT_IN: Condition applies when user does NOT match the value
- SWIMLANE_OWNER: Current swimlane owner (automatic, no value needed)
- PROCESS_DATA: Reference data stored in the process instance
- CONFIGURATION_SWIMLANE_ROLE: Use roles configured at swimlane level
- PROCESS_DATA: Process data keypath (e.g.,
${app.client.userList}) - CONFIGURATION_SWIMLANE_ROLE: Array of role names (e.g.,
["ROLE_1", "ROLE_2"]) - SWIMLANE_OWNER: Not applicable (determined automatically)
6
Save configuration
Click Save to apply your permission-based expression. Test the behavior by accessing the process with different user roles.
Common expression patterns
Use these examples as templates for typical permission scenarios:Role-based access control
Hide or disable elements for specific roles configured at the swimlane level:Dynamic username lists
Control access based on usernames stored in process data:Swimlane owner restrictions
Limit access to the current swimlane owner only:Exclusion patterns
Hide elements from specific users or roles usingNOT_IN:
Advanced: Cross-swimlane references
Limitation
SWIMLANE_OWNER references only the owner of the current swimlane. You cannot directly reference owners from other swimlanes in the same process.
Workaround: Store owners in process data
To reference users from other swimlanes, explicitly store their information in process data during swimlane transitions:- Add a Business Rule node at the start of each swimlane
- Capture the current user’s username
- Store it in your process data structure (e.g.,
swimlaneOwners.{swimlaneName}) - Reference this stored data in permission expressions on other swimlanes

